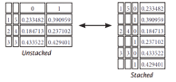
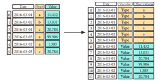
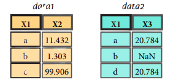
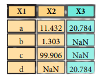
Pandas Cheat Sheet: Data Wrangling in Python
This cheat sheet is a quick reference for data wrangling with Pandas, complete with code samples.
Jun 2021 · 4 min read
RelatedSee MoreSee More
cheat sheet
Pandas Cheat Sheet for Data Science in Python
A quick guide to the basics of the Python data analysis library Pandas, including code samples.
Karlijn Willems
4 min
cheat sheet
Python for Data Science - A Cheat Sheet for Beginners
This handy one-page reference presents the Python basics that you need to do data science
Karlijn Willems
4 min
cheat sheet
NumPy Cheat Sheet: Data Analysis in Python
This Python cheat sheet is a quick reference for NumPy beginners.
Karlijn Willems
6 min
cheat sheet
Python For Data Science Cheat Sheet For Beginners
This cheat sheet covers the basics that you need to know to do data science with Python
Karlijn Willems
1 min
tutorial
Python For Data Science - A Cheat Sheet For Beginners
This handy one-page reference presents the Python basics that you need to do data science
Karlijn Willems
7 min
tutorial
Pandas Tutorial: DataFrames in Python
Explore data analysis with Python. Pandas DataFrames make manipulating your data easy, from selecting or replacing columns and indices to reshaping your data.
Karlijn Willems
20 min