PyTorch is an open-source and community-led deep learning framework that provides a flexible and efficient way of building machine learning models. It has a user-friendly interface, extensive community support, and seamless integration with the Python ecosystem.
PyTorch 2.0 has introduced fundamental changes to the core compiler operations while preserving the same level of familiarity and ease for developers. This latest enhancement promises accelerated performance and expanded support for Dynamic Shapes and Distributed.
What is New in PyTorch 2.0?
PyTorch is moving parts from C++ back into Python, making it faster and hackable. With version 2.0, they have introduced `torch.compile`, which has changed how PyTorch operates at the compiler level. This feature is optional and does not affect your old code.
PyTorch 2.0 Compile
To provide a solid foundation for the `torch.compile` feature, new technologies were introduced:
- TorchDynamo. A Python-level Just-in-Time (JIT) compiler specifically designed to accelerate PyTorch. By integrating with the frame evaluation API in CPython, it dynamically modifies Python bytecode at runtime, enabling faster execution of code.
- AOTAutograd. A toolkit for assisting developers in accelerating model training on PyTorch. It traces both the forward and backward graphs in advance. Moreover, AOTAutograd offers simple mechanisms to compile the extracted graphs seamlessly using cutting-edge deep-learning compilers.
- PrimTorch. By significantly reducing the number of PyTorch operators from over 2000 to a concise set of approximately 250 primitive operators, PrimTorch has remarkably simplified the process of developing PyTorch features or backends.
- TorchInductor. A PyTorch-native deep learning compiler that automatically maps PyTorch models into generated code for multiple accelerators and backends. TorchInductor uses OpenAI Triton as a building block for GPU acceleration.
All of the new technologies are written in Python and support Dynamic shapes. It makes new PyTorch run code faster, more flexible, and easily hackable, lowering the barrier of entry.
Code Examples
Let us review the quick and easy code implementation of PyTorch Compiler.
Without torch.compile
import torch
model = torch.hub.load("pytorch/vision", "resnet50", weights="IMAGENET1K_V2")Without torch.compile
To boost model performance, just add the torch.compile wrapper around the model and get a compiled model. It is plug-and-play.
import torch
model = torch.hub.load("pytorch/vision", "resnet50", weights="IMAGENET1K_V2")
compiled_model = torch.compile(model)Learn to build deep learning models with the PyTorch library by taking Deep Learning with PyTorch course.
You can simply train your model without changing a thing.
import torch
model = torch.compile(model)
for batch in dataloader:
run_epoch(model, batch)Or you can run mode inference.
model = torch.compile(model)
model(**input)The torch.compile() come with additional parameters:
- mode: you can specify what compiler should optimize while compiling.
- dynamic: it is used to enable the code path for Dynamic Shapes.
- fullgraph: it compiles the program into a single graph.
- backend: by default it uses TorchInductor, but you can specify other available compiler backends.
def torch.compile(model: Callable,
*,
mode: Optional[str] = "default",
dynamic: bool = False,
fullgraph:bool = False,
backend: Union[str, Callable] = "inductor",
**kwargs
) -> torch._dynamo.NNOptimizedModuleLearn the basics of PyTorch API and create a simple neural network from scratch using our PyTorch Tutorial.
Benchmark
In getting started with PyTorch 2.0, developers have used 163 open-source (46 HuggingFace Transformers, 61 TIMM, and 56 TorchBench) models for creating performance benchmarks of a new compile feature. The Benchmark includes tasks such as benchmark carefully to include tasks such as Image classification, Image generation, Language modeling, Recommender systems, and Reinforcement learning.
The result shows significantly improved performance while training on NVIDIA A100 GPUs.
Note: currently, the default backend only supports CPUs and Nvidia Volta and Ampere GPUs series.
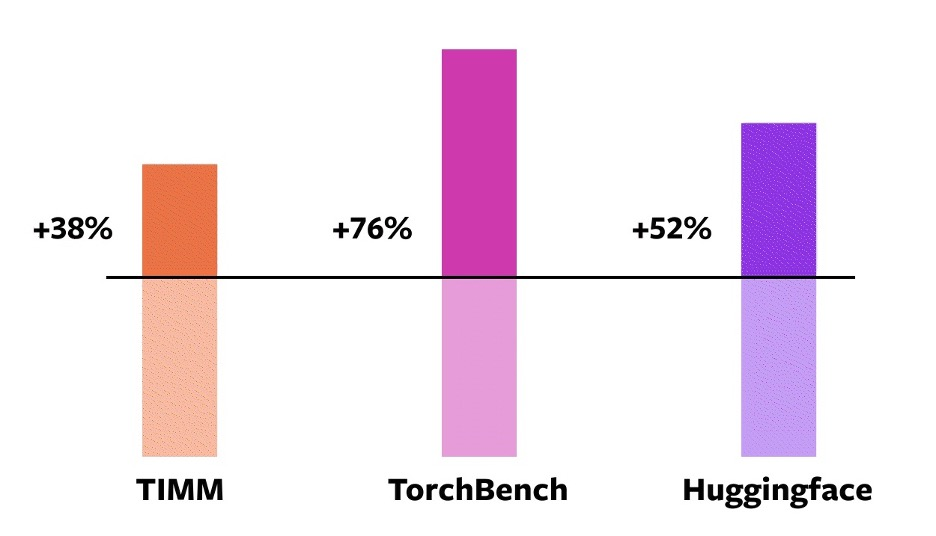
PyTorch compiler benchmark on NVIDIA A100 GPU
It is a start, and you will see in the upcoming update more performance and scalability enhancements.
How to Install PyTorch 2.0
You can simply install a newer version of PyTorch by using pip.
Copy and paste the below command into your terminal.
For GPUs: CUDA 11.8
It turns out that the newer version of GPUs have shown drastically better performance.
pip3 install numpy --pre torch torchvision torchaudio --force-reinstall --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/cu118For GPUs: CUDA 11.7
pip3 install numpy --pre torch torchvision torchaudio --force-reinstall --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/cu117For CPUs:
pip3 install numpy --pre torch torchvision torchaudio --force-reinstall --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/cpuFor Verification:
git clone https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch
cd tools/dynamo
python verify_dynamo.pyAccelerating Hugging Face with PyTorch 2.0
Let’s try the torch.compile function to accelerate Hugging Face transformers. You can make your Hugging Face code run faster with a single-line decorator.
Note: With torch.compile(), we have seen a 30%-200% performance boost on training - TorchDynamo Performance Dashboard.
In this example, we will apply torch.compile on a “dolly-v2-3b" large language model for faster inference. To run the code in Google Colab, we have to first install the necessary Python libraries.
%%capture
%pip install transformers accelerate xformersThen, we will download and load the tokenizer and language model using Hugging Face transformers. After that, we will add nn.Module to the torch.compile() function.
import torch
from transformers import (
AutoTokenizer,
AutoModelForCausalLM,
GenerationConfig,
pipeline,
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("databricks/dolly-v2-3b")
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"databricks/dolly-v2-3b", device_map="auto", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16
)
model = torch.compile(model) #only line of code is requiredIn the final step, we will convert text into tokens using tokenizer, feed it to model.generate, and then decode the generated output into text using tokenizer.batch_decode.
prompt = "I love you because"
inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").to(device="cuda:0")
# Generate
generate_ids = model.generate(inputs.input_ids, max_length=50)
tokenizer.batch_decode(
generate_ids, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=True
)[0]As we can see, the “dolly-v2” has completed the sentence by adding, “you are a good person…”
"I love you because you are a good person.
You are kind, you help others, you are honest, you are loyal, you are humble, you are humble, you are humble.
You are a good person."It also works with the Hugging Face pipeline. Just provided a task type, model, and tokenizer.
generator = pipeline("text-generation", model= model,tokenizer=tokenizer)
generator("What is the name of Germany's Capital?")Output:
[{'generated_text': "What is the name of Germany's Capital?
The name of Germany's Capital is Berlin."}]The compile function works out of the box with transformers, accelerate, and TIMM Python libraries.
If you're uncertain about where to begin your deep learning and AI career, the Machine Learning Scientist with Python career track is an excellent starting point. It provides a comprehensive overview of crucial Python skills that can help you secure a job as a machine learning scientist.
As a certified data scientist, I am passionate about leveraging cutting-edge technology to create innovative machine learning applications. With a strong background in speech recognition, data analysis and reporting, MLOps, conversational AI, and NLP, I have honed my skills in developing intelligent systems that can make a real impact. In addition to my technical expertise, I am also a skilled communicator with a talent for distilling complex concepts into clear and concise language. As a result, I have become a sought-after blogger on data science, sharing my insights and experiences with a growing community of fellow data professionals. Currently, I am focusing on content creation and editing, working with large language models to develop powerful and engaging content that can help businesses and individuals alike make the most of their data.
blog
Pandas 2.0: What’s New and Top Tips
cheat sheet
Deep Learning with PyTorch Cheat Sheet
tutorial
NumPy 2.0 Release: Key Changes and Migration
tutorial
Ten Important Updates from TensorFlow 2.0
tutorial
Dropout Regularization Using PyTorch: A Hands-On Guide
tutorial