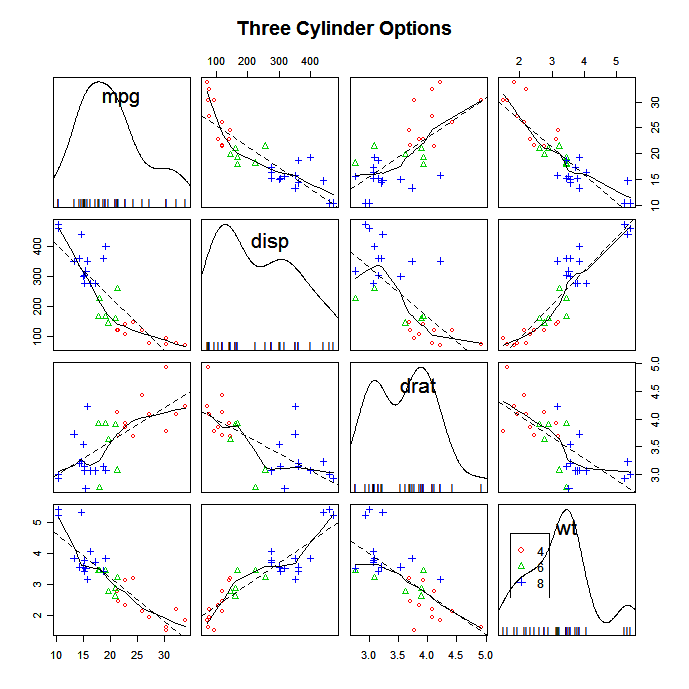
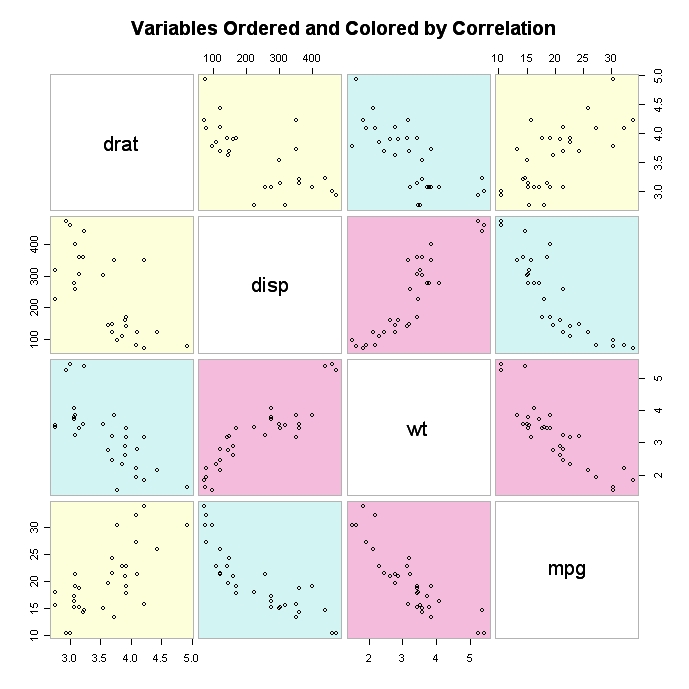
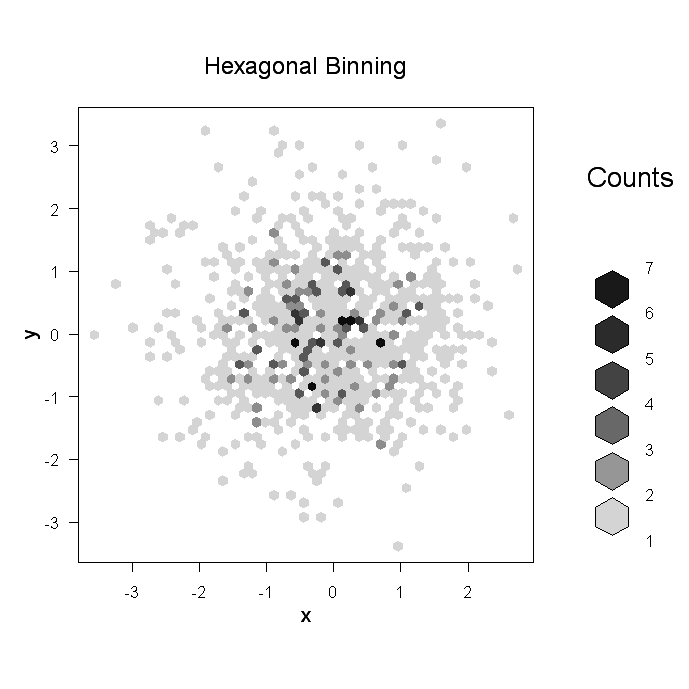
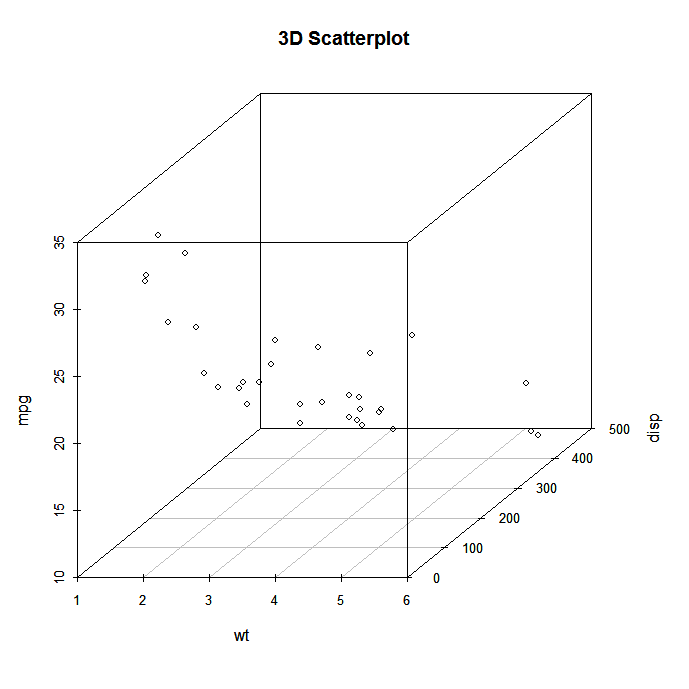
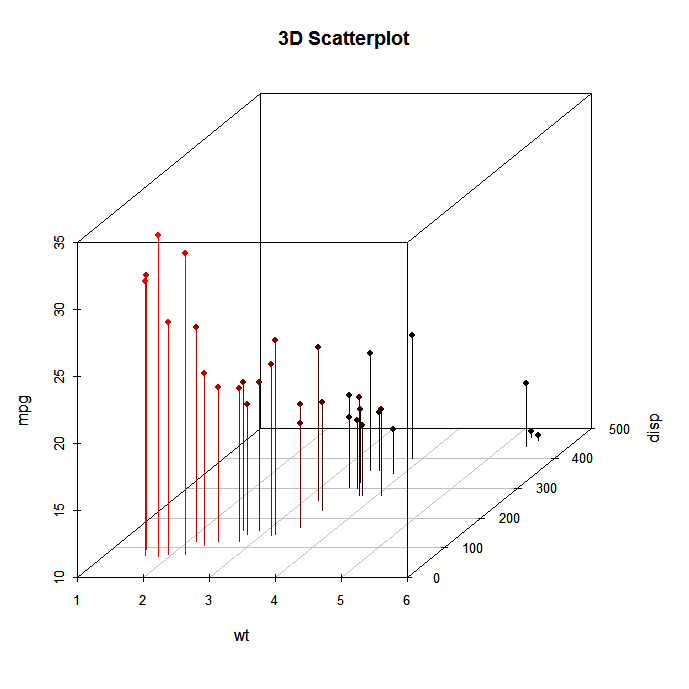
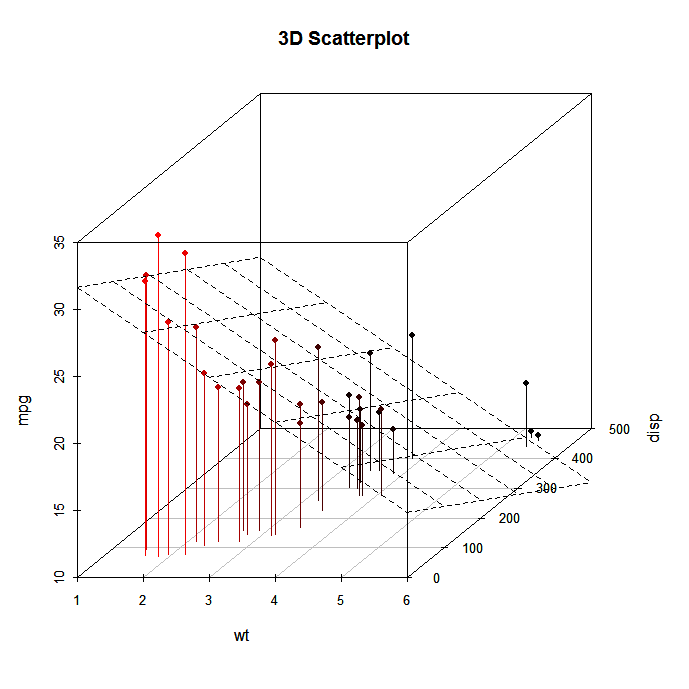
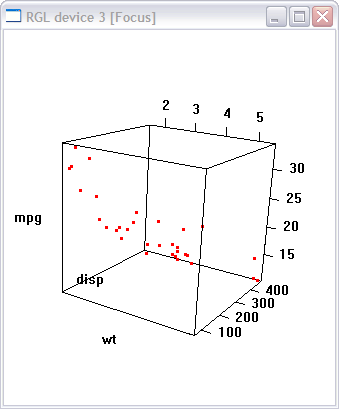
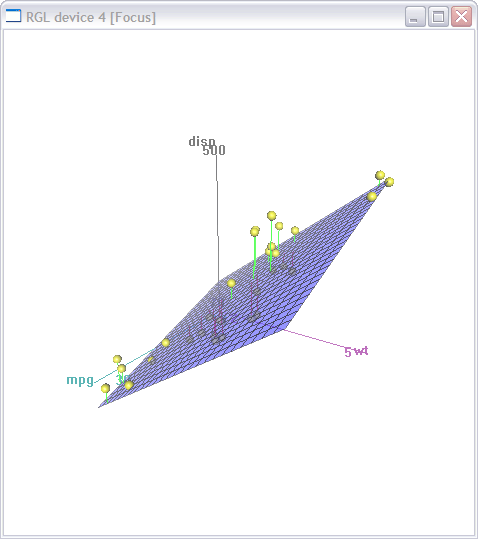
Scatterplot in R
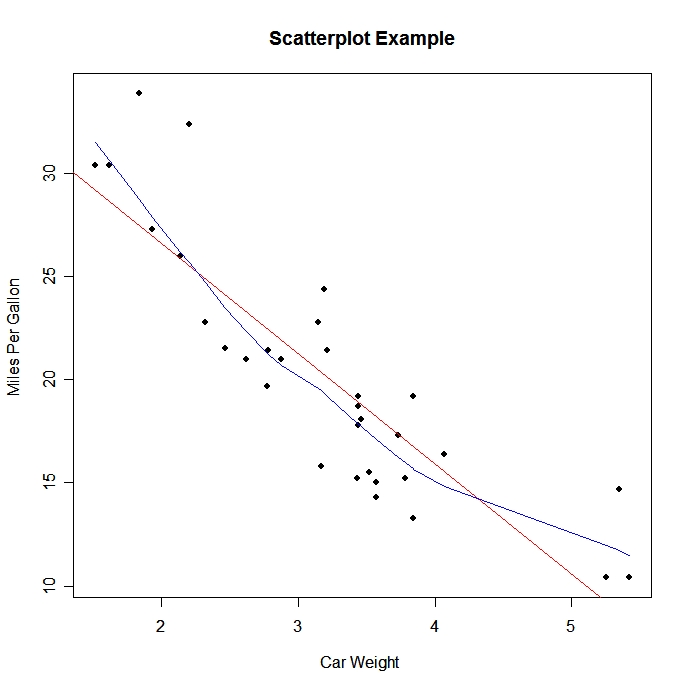
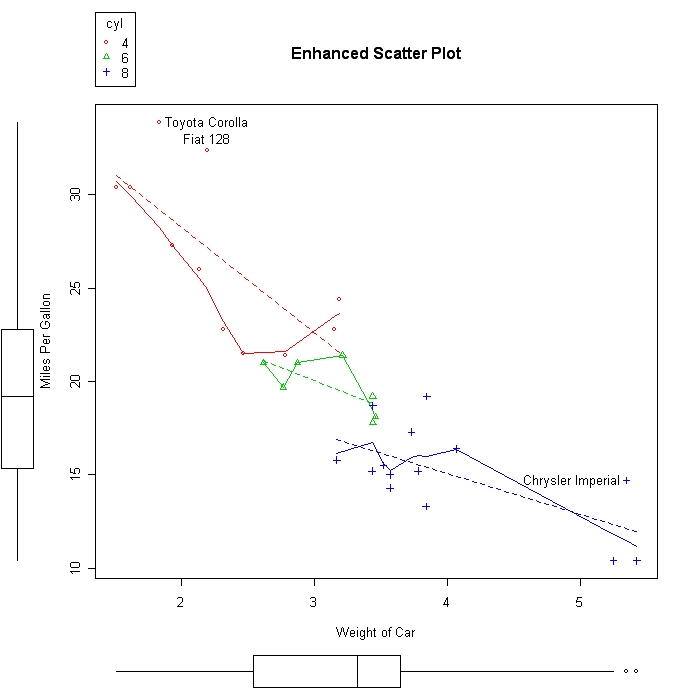
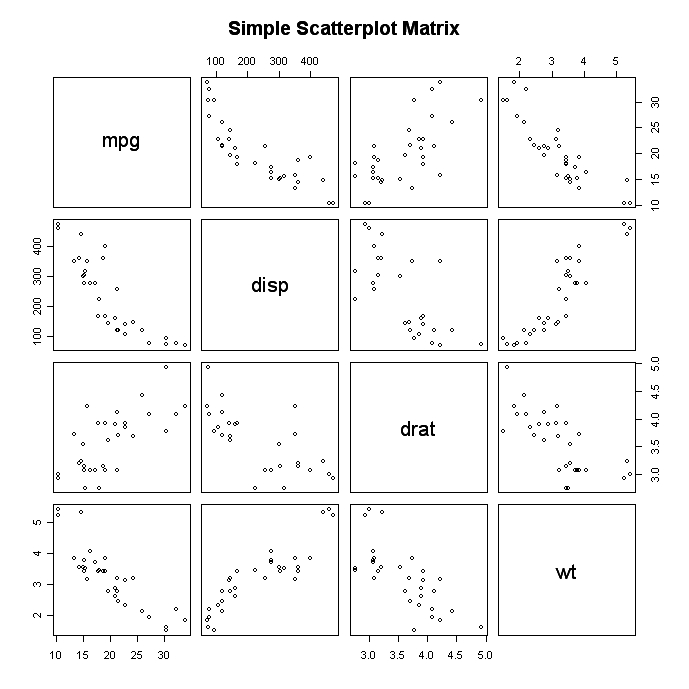
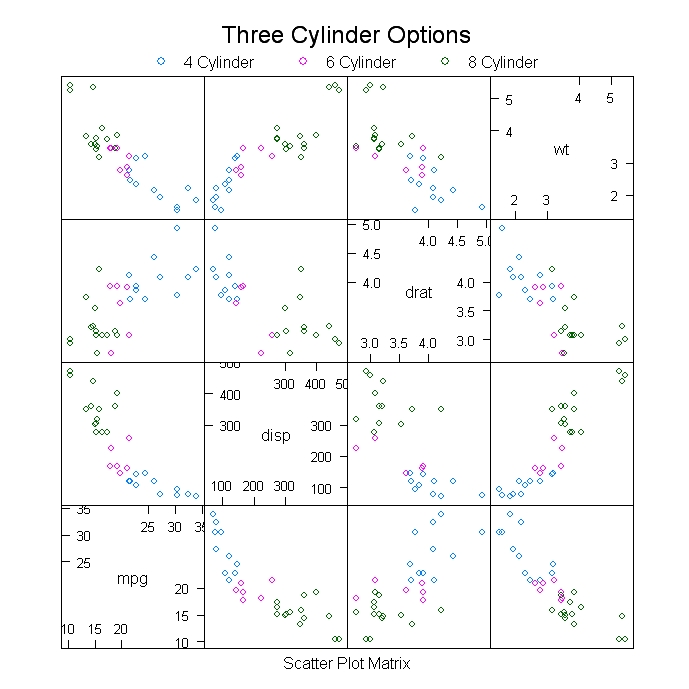
Learn how to create a scatterplot in R. The basic function is plot(x, y), where x and y are numeric vectors denoting the (x,y) points to plot.
Mar 2024
RelatedSee MoreSee More
blog
R Correlation Tutorial
Get introduced to the basics of correlation in R: learn more about correlation coefficients, correlation matrices, plotting correlations, etc.
David Woods
18 min
tutorial
How to Make a ggplot2 Histogram in R
Learn how to make a ggplot2 histogram in R. Make histograms in R based on the grammar of graphics.
Kevin Babitz
15 min
tutorial
Bivariate Distribution Heatmaps in R
Learn how to visually show the relationship between two features, how they interact with each other, and where data points are concentrated.
Carlos Zelada
6 min
tutorial
15 Questions All R Users Have About Plots
There are different types of R plots, ranging from the basic graph types to complex types of graphs. Here we discover how to create these.
Karlijn Willems
39 min
tutorial
R Formula Tutorial
Discover the R formula and how you can use it in modeling- and graphical functions of well-known packages such as stats, and ggplot2.
Karlijn Willems
33 min
tutorial
Box Plot in R Tutorial
Learn about box plots in R, including what they are, when you should use them, how to implement them, and how they differ from histograms.
DataCamp Team
4 min