course
Topics
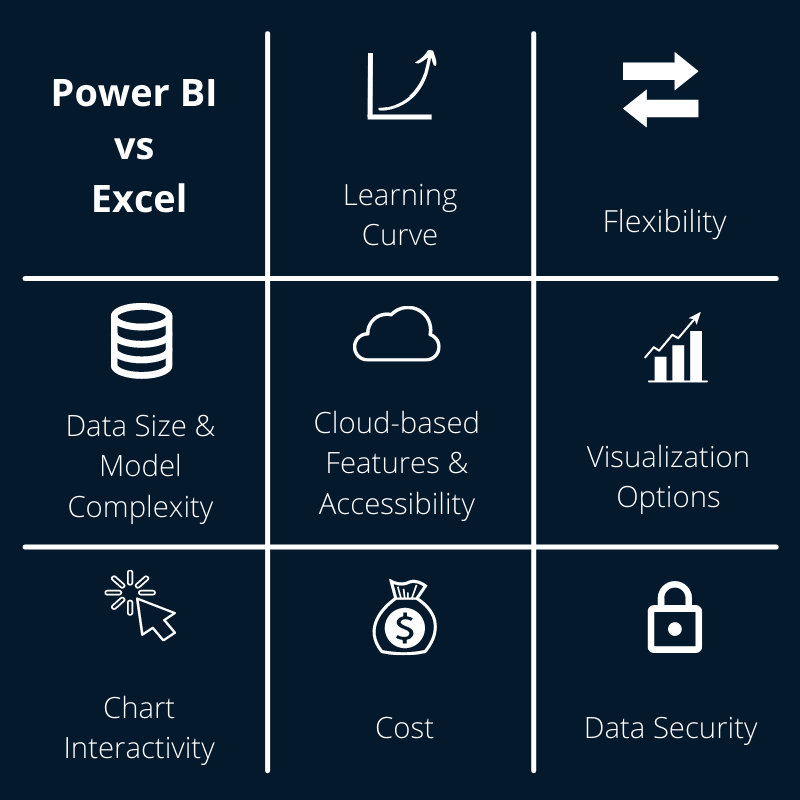
Courses for Power Bi and Excel
3 hours
39.2K
course
Introduction to Power BI
4 hours
373.9K
course
Data Preparation in Power BI
3 hours
32.5K
See More
RelatedSee MoreSee More
blog
Power BI vs Alteryx: Which Should You Use?
Explore the key differences between Power BI and Alteryx in user interface, integration, cost, and learning curve to determine the best fit for your needs.
Vikash Singh
8 min
blog
Looker Studio vs Power BI: Which One Should You Use?
Explore the key differences between two popular business intelligence tools: Looker Studio and Power BI. Determine which one is best fit for your needs.
Laiba Siddiqui
8 min
blog
Power BI vs Tableau: Which is The Better Business Intelligence Tool in 2024?
Power BI or Tableau? This comparison will help you decide which of these tools to use for your data science and analytics needs.
Shaun Edmond
7 min
blog
How to Transition From Excel to Power BI
Interested in learning Power BI but don't know where to start? Read this guide for step-by-step learning and resources to keep practicing what you learned
Eugenia Anello
11 min
blog
How to Export Power BI Data to Excel
Wish you could see the data behind your Power BI visualizations? Here’s our guide to exporting Power BI data to Excel.
Eugenia Anello
6 min
tutorial
Power BI Dashboards vs Reports: A Comprehensive Guide
Explore the key differences and unique features of Power BI dashboards and reports. Learn how to leverage both tools effectively for data analysis, visualization, and decision-making.
Maarten Van den Broeck
8 min